|
|
 |

RAM
RAM is the acronym for random access memory. RAM is also known as working memory or main memory.
RAM is a component of every computer and is required by the processor. Frequently requested data is stored in RAM, such as, for example, an image that the user is editing.
The operating system that is a component of every computer increases main memory requirements, since the operating system in particular uses a lot of data frequently.
If the users wants to view an image as well, there must be additional space in the main memory, so that the system can add the image. If the available main memory capacity is insufficient, a paging file must be used. This significantly reduces processing speed and thus should be avoided.
RAM physically consists of memory chips (that differ from a hard disk), which means that additional main memory capacity is more expensive than comparable hard disk capacity. That is why 128 MB and more is currently common.
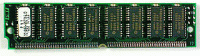
SIMM with 72 pins | 
Commonly used DIMM with 168 pins | 
DDR-RAM module with 184 pins | 
Rambus module, also with 184 pins | 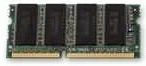
DIMM with 144 pins for notebooks |
Back
|
 |
|




